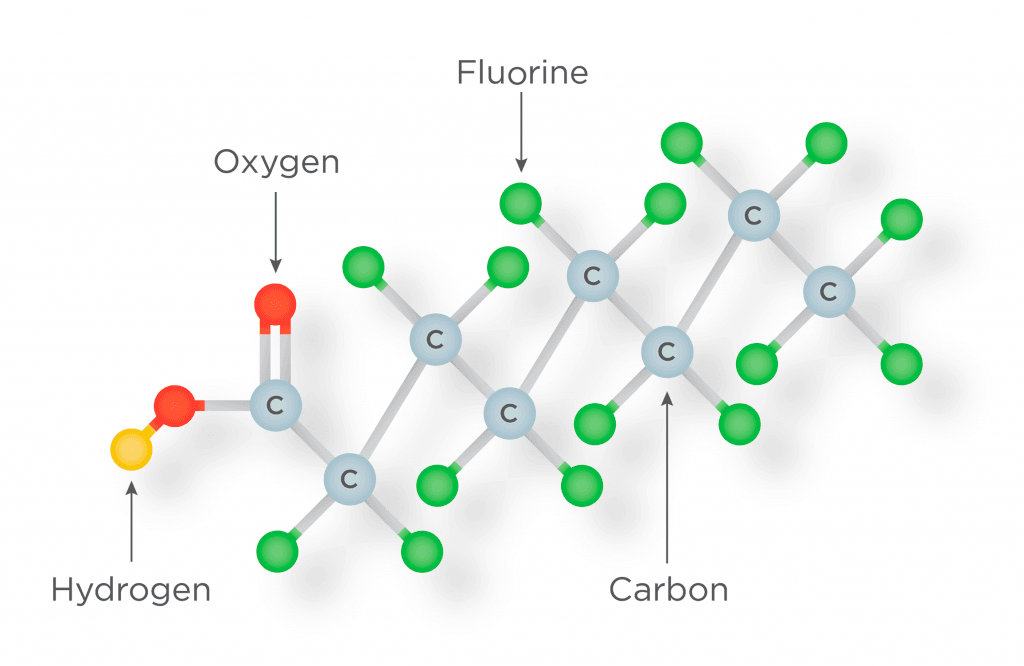
Chemical Composition
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances are....
Chemical Composition of Perfluorooctanic Acid (PFOA) Source from Communities Unlimited.
A man-made chemical family which include more than 9,000 combinations of the same Carbon-Fluorine bond.
The Carbon-Fluorine bond has fluorine (high electronegativity) atoms linked to various chains of carbon atoms, and that bond is considered unbreakable (surfactant-like and bioaccumulative).
PFAS Family Tree
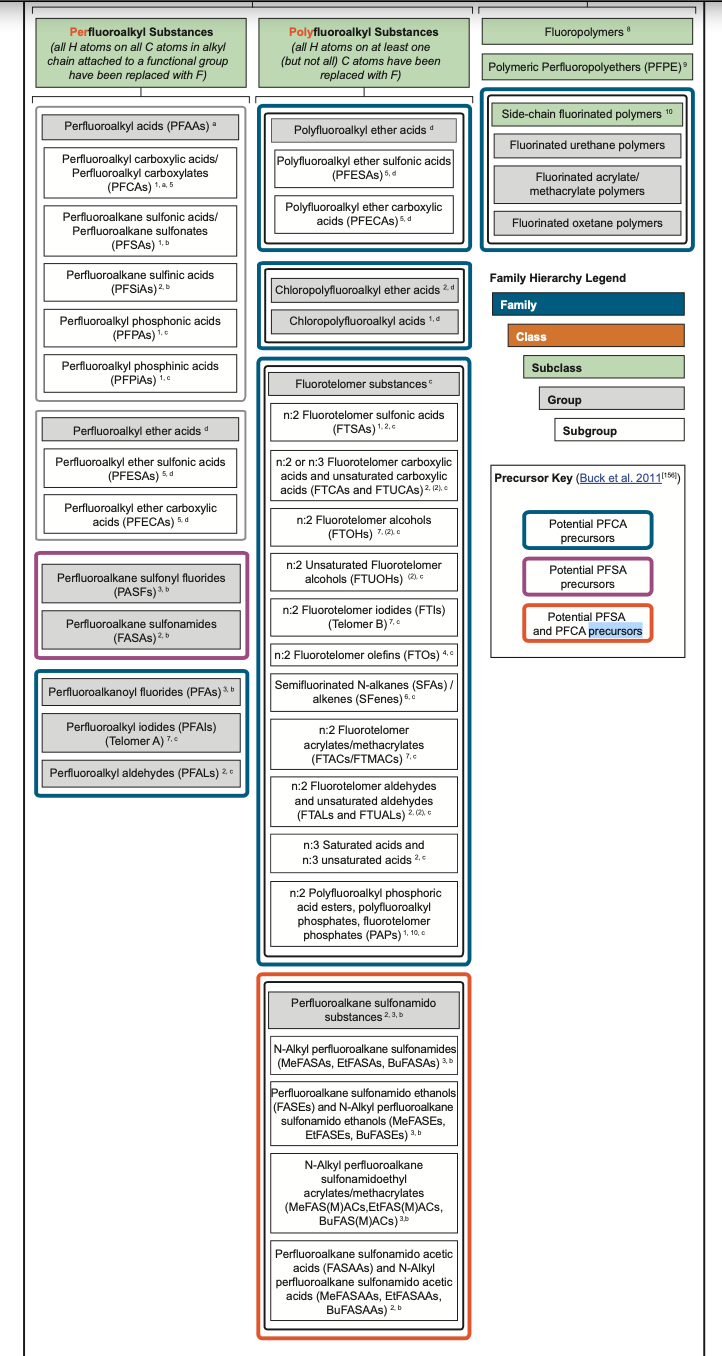
Source from Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council (ITRC).
PFAS is considered a family of chemicals, which then are divided into class, then subclass, groups, and then subgroups. The bio-accumulative PFAS in our bodies and the environment are in the Nonpolymers class. There are the C8 long chain PFAS, the C6 semi-long chain PFAS, and also the C4 short chain PFAS.
Perfluoroalkyl – Alkyl straight-chain carbon backbone is fully fluorinated (All hydrogens replaced with fluorine)
Polyfluoroalkyl – Somewhat fluorinated (Firefighting foams)
The PFAAs group includes the well known PFOA and PFOS forms of PFAS. GenX chemicals are part of PFECAs, with one being ammonium salt and they were made as a replacement of PFOA and PFOS.
With more compositions of PFAS being created, it is becoming harder and harder to control.