TweetyNet
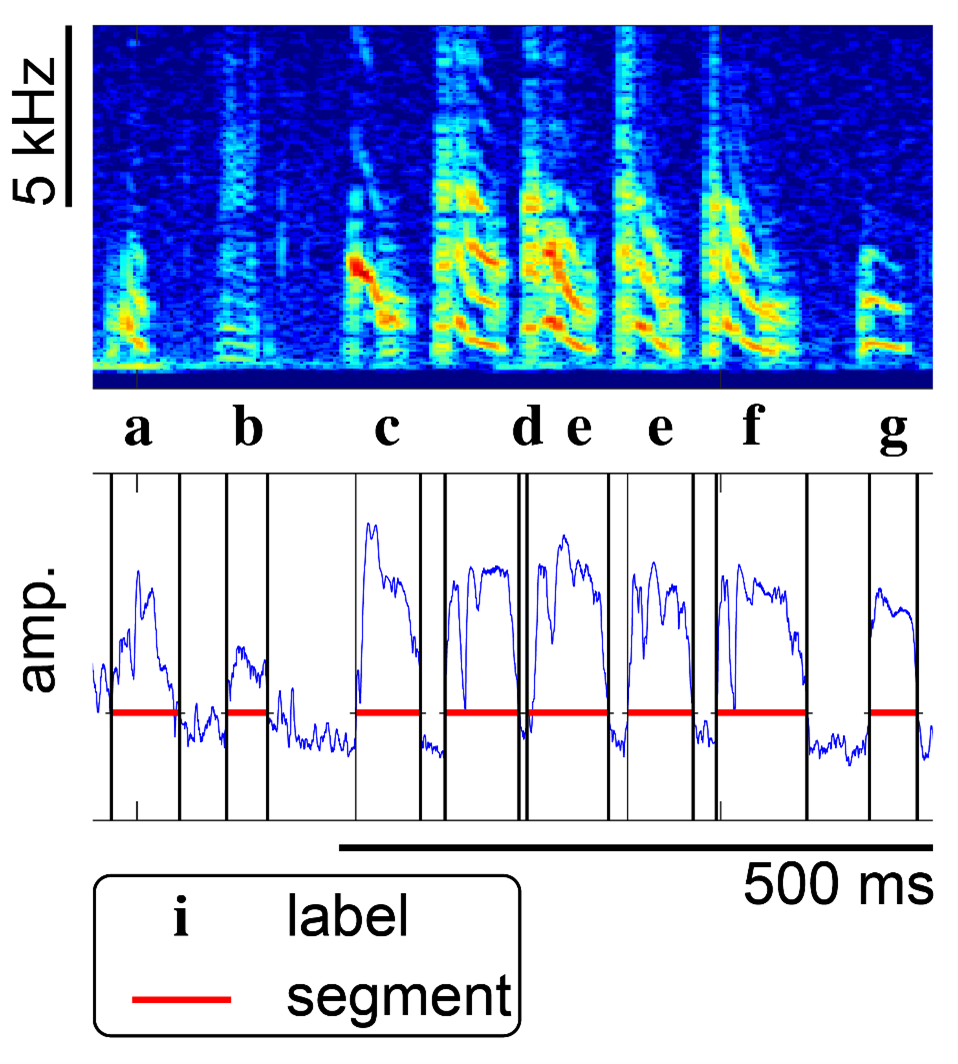
Songbirds are a commonly used model to study sensory-motor learning and production of sequential behavior as birdsong resembles human speech in key areas. This includes being learned by imitation, being culturally transmitted, and consisting of vocal gestures executed in a sequence. However, analyzing birdsong at the level of syllables requires large amounts of data to be manually annotated which is labor intensive. Thus, Yarden Cohen, David Nicholson and colleagues developed TweetyNet, a deep neural network that learns directly from spectrograms to annotate each bird’s unique song.
TweetyNet has been validated on two species, Bengalese finches and canaries, and replicated previous findings from behavioral studies. The group also provide open-source software and a large repository of birdsong recordings that can be used for benchmarking. The quick annotating provided by TweetyNet allows for larger datasets to be analyzed, allowing for new questions to be answered. Thus, TweetyNet is an important step forward in birdsong sensorimotor research.
This research tool was created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the tool was described, and include an RRID in the Materials and Methods of your future publications. RRID:SCR_022360
Read the Paper!
Read more about TweetyNet in the eLife paper!
GitHub Repository
Get access to necessary files and code for TweetyNet from their GitHub repository!