WRAQ
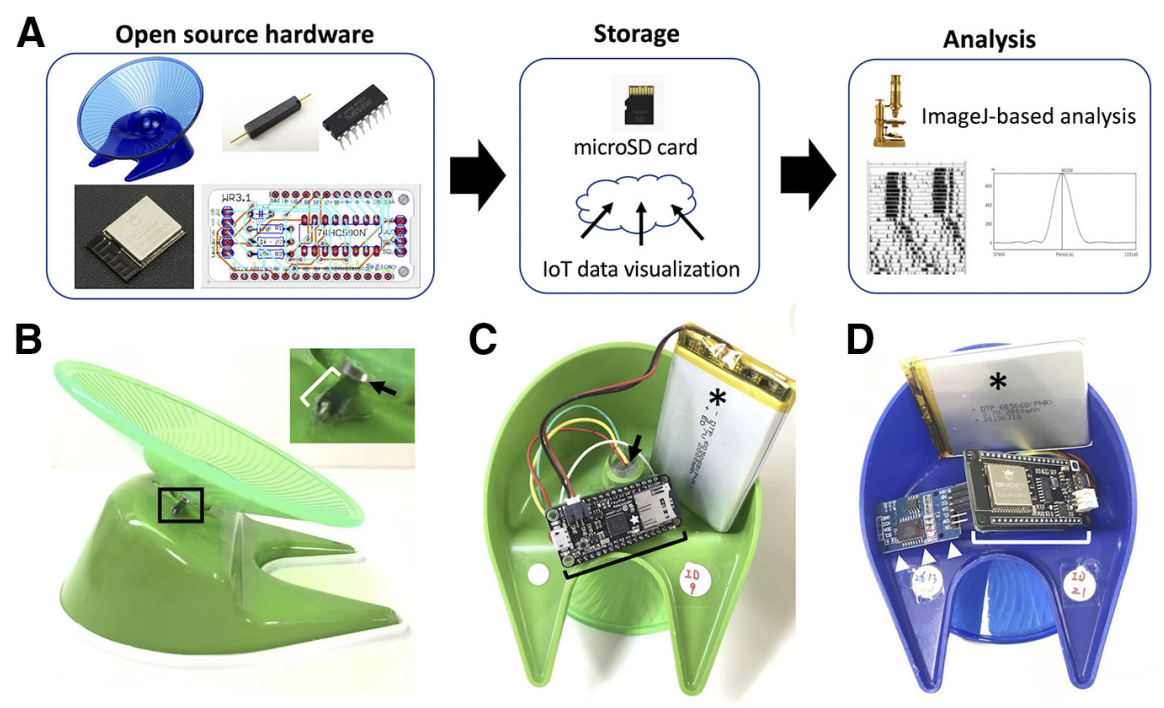
Melina Zhu, Deepa Kamath Kasaragod, and colleagues at the department of Neurobiology at the Hiroshima University in Japan, developed a device called the wheel-running activity acquisition (WRAQ) system. It track the circadian rhythms of rodents using a microcontroller, powered by a lithium polymer battery, and surveys exercise activity for up to 30 days. Data can be stored on a microSD card or using an online server using a WiFi connection. Python software is provide to interface the system with ActogramJ to analyze chronobiological aspects of the data. A link is provided below to the design files and documentation on programming WRAQ using Python. Most commonly used in neuroscience studies with rodent subjects, the WRAQ apparatus is a cost-effective way to monitor wheel-running activity of rodents in caged environments.
This research tool was created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the tool was described, and include an RRID in the Materials and Methods of your future publications. RRID: SCR_023353
Special thanks to Kevin Calderón, an undergraduate neuroscience major, for providing this project summary! This summary is part of a collection from students in a Computational Methods for Neuroscience Course at American University.
Access WRAQ on GitHub
Check out the WRAQ GitHub repository.
Read the paper!
Learn more about WRAQ on eNeuro!






