Despite the prevalence of online learning today, it is often viewed as a less favorable option when compared to the traditional, in-person educational experience. Criticisms of online learning come from various sectors, like employer groups, college faculty, and the general public, and generally includes a lack of perceived quality as well as rigor. Additionally, some students report feelings of social isolation in online learning (Protopsaltis & Baum, 2019).
In my experience as an online student as well as an online educator, online learning has been just the opposite. I have been teaching in a fully online master’s degree program for the last three years and have found it to be a rich and rewarding experience for students and faculty alike. As an instructor, I have felt more connected to and engaged with my online students when compared to in-person students. I have also found that students are actively engaged with course content and demonstrate evidence of higher-order thinking through their work. Students report high levels of satisfaction with their experiences in online learning as well as the program overall as indicated in their Student Evaluations of Teaching (SET) at the end of every course. I believe that intelligent course design, in addition to my engagement in professional development related to teaching and learning online, has greatly influenced my experience.
In an article by Wiley Education Services, authors identified the top six challenges facing US institutions of higher education, and include:
- Declining student enrollment
- Financial difficulties
- Fewer high school graduates
- Decreased state funding
- Lower world rankings
- Declining international student enrollments
Of the strategies that institutions are exploring to remedy these issues, online learning is reported to be a key focus for many universities (“Top Challenges Facing US Higher Education”, n.d.).
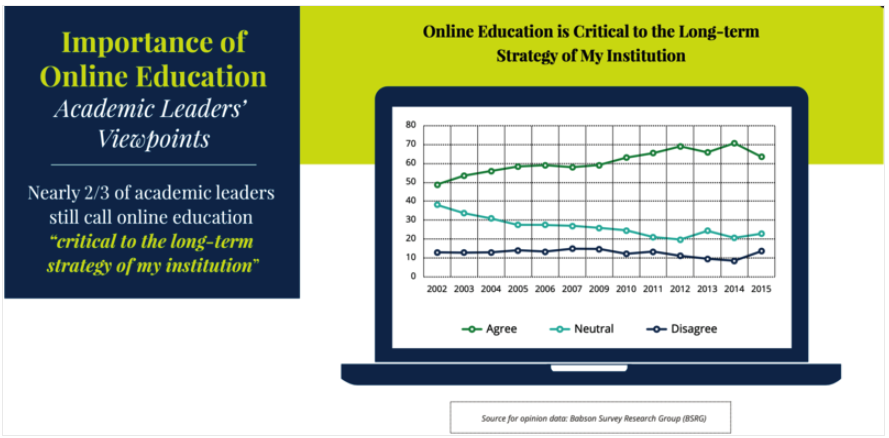
Babson Survey Research Group, 2016, [PDF file].
Some of the questions I would like to explore in further research include:
- What factors influence engagement and connection in distance education?
- Are the learning outcomes in online education any different than the outcomes achieved in a traditional classroom setting?
- How do course design and instructor training influence these factors?
- In what ways might educational technology tools enhance the overall experience for students and instructors alike?
In this literature review, I have chosen to focus on a comparison of student learning outcomes in online education versus the traditional classroom setting. My hope is that this research will unlock the answers to some of the additional questions posed above and provide additional direction for future research.
Online Learning Defined
According to Mayadas, Miller, and Sener (2015), online courses are defined by all course activity taking place online with no required in-person sessions or on-campus activity. It is important to note, however, that the Babson Survey Research Group, a prominent organization known for their surveys and research in online learning, defines online learning as a course in which 80-100% occurs online. While this distinction was made in an effort to provide consistency in surveys year over year, most institutions continue to define online learning as learning that occurs 100% online.
Blended or hybrid learning is defined by courses that mix face to face meetings, sessions, or activities with online work. The ratio of online to classroom activity is often determined by the label in which the course is given. For example, a blended classroom course would likely include more time spent in the classroom, with the remaining work occurring outside of the classroom with the assistance of technology. On the other hand, a blended online course would contain a greater percentage of work done online, with some required in-person sessions or meetings (Mayadas, Miller, & Sener, 2015).
A classroom course (also referred to as a traditional course) refers to course activity that is anchored to a regular meeting time.
Enrollment Trends in Online Education
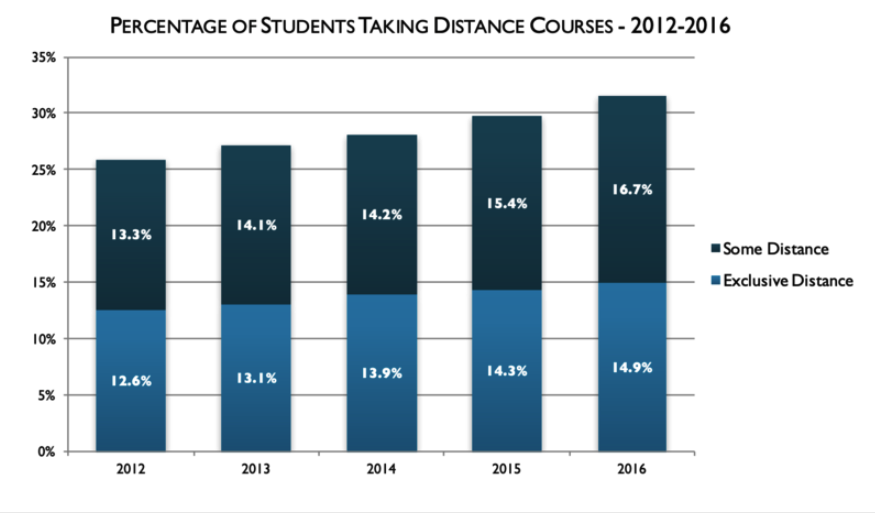
There has been an upward trend in the number of postsecondary students enrolled in online courses in the U.S. since 2002. A report by the Babson Survey Research Group showed that in 2016, more than six million students were enrolled in at least one online course. This number accounted for 31.6% of all college students (Seaman, Allen, & Seaman, 2018). Approximately one in three students are enrolled in online courses with no in-person component. Of these students, 47% take classes in a fully online program. The remaining 53% take some, but not all courses online (Protopsaltis & Baum, 2019).
Perceptions of Online Education
In a 2016 report by the Babson Survey Research Group, surveys of faculty between 2002-2015 showed approval ratings regarding the value and legitimacy of online education ranged from 28-34 percent. While numbers have increased and decreased over the thirteen-year time frame, faculty approval was at 29 percent in 2015, just 1 percent higher than the approval ratings noted in 2002 – indicating that perceptions have remained relatively unchanged over the years (Allen, Seaman, Poulin, & Straut, 2016).
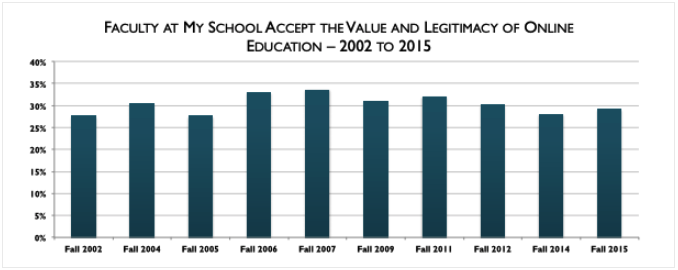
(Allen, I.E., Seaman, J., Poulin, R., Taylor Strout, T., 2016, p. 26)
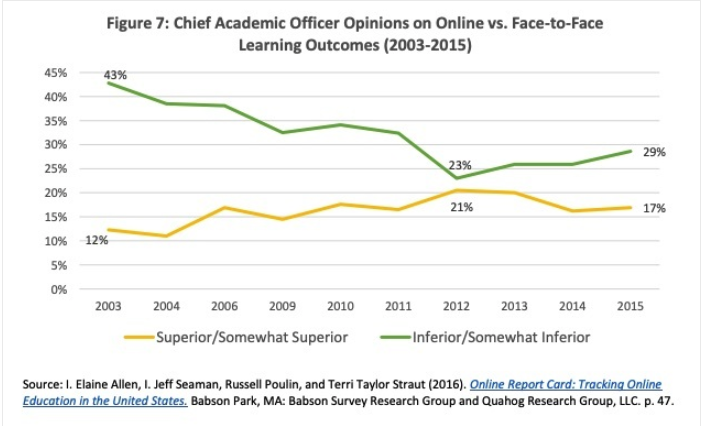
In a separate survey of chief academic officers, perceptions of online learning appeared to align with that of faculty. In this survey, leaders were asked to rate their perceived quality of learning outcomes in online learning when compared to traditional in-person settings. While the percentage of leaders rating online learning as “inferior” or “somewhat inferior” to traditional face-to-face courses dropped from 43 percent to 23 percent between 2003 to 2012, the number rose again to 29 percent in 2015 (Allen, Seaman, Poulin, & Straut, 2016).
Faculty and academic leaders in higher education are not alone when it comes to perceptions of inferiority when compared to traditional classroom instruction. A 2013 Gallop poll assessing public perceptions showed that respondents rated online education as “worse” in five of the seven categories seen in the table below.
In general, Americans believed that online education provides both lower quality and less individualized instruction and less rigorous testing and grading when compared to the traditional classroom setting. In addition, respondents also thought that employers would perceive a degree from an online program less positively when compared to a degree obtained through traditional classroom instruction (Saad, Busteed, & Ogisi, 2013).
Student Perceptions of Online Learning
So what do students have to say about online learning? In Online College Students 2015: Comprehensive Data on Demands and Preferences, 1500 college students who were either enrolled or planning to enroll in a fully online undergraduate, graduate, or certificate program were surveyed. 78 percent of students believed the academic quality of their online learning experience to be better than or equal to their experiences with traditional classroom learning. Furthermore, 30 percent of online students polled said that they would likely not attend classes face to face if their program were not available online (Clienfelter & Aslanian, 2015). The following video describes some of the common reasons why students choose to attend college online.
How Online Learning Affects the Lives of Students (Pearson North America, 2018, June 25)
In a 2015 study comparing student perceptions of online learning with face to face learning, researchers found that the majority of students surveyed expressed a preference for traditional face to face classes. A content analysis of the findings, however, brought attention to two key ideas: 1) student opinions of online learning may be based on “old typology of distance education” (Tichavsky, et al, 2015, p.6) as opposed to actual experience, and 2) a student’s inclination to choose one form over another is connected to issues of teaching presence and self-regulated learning (Tichavsky et al, 2015).
Student Learning Outcomes
Given the upward trend in student enrollment in online courses in postsecondary schools and the steady ratings of the low perceived value of online learning by stakeholder groups, it should be no surprise that there is a large body of literature comparing student learning outcomes in online classes to the traditional classroom environment.
While a majority of the studies reviewed found no significant difference in learning outcomes when comparing online to traditional courses (Cavanaugh & Jacquemin, 2015; Kemp & Grieve, 2014; Lyke & Frank 2012; Nichols, Shaffer, & Shockey, 2003; Stack, 2015; Summers, Waigandt, & Whittaker, 2005), there were a few outliers. In a 2019 report by Protopsaltis & Baum, authors confirmed that while learning is often found to be similar between the two mediums, students “with weak academic preparation and those from low-income and underrepresented backgrounds consistently underperform in fully-online environments” (Protopsaltis & Baum, 2019, n.p.). An important consideration, however, is that these findings are primarily based on students enrolled in online courses at the community college level – a demographic with a historically high rate of attrition compared to students attending four-year institutions (Ashby, Sadera, & McNary, 2011). Furthermore, students enrolled in online courses have been shown to have a 10 – 20 percent increase in attrition over their peers who are enrolled in traditional classroom instruction (Angelino, Williams, & Natvig, 2007). Therefore, attrition may be a key contributor to the lack of achievement seen in this subgroup of students enrolled in online education.
In contrast, there were a small number of studies that showed that online students tend to outperform those enrolled in traditional classroom instruction. One study, in particular, found a significant difference in test scores for students enrolled in an online, undergraduate business course. The confounding variable, in this case, was age. Researchers found a significant difference in performance in nontraditional age students over their traditional age counterparts. Authors concluded that older students may elect to take online classes for practical reasons related to outside work schedules, and this may, in turn, contribute to the learning that occurs overall (Slover & Mandernach, 2018).
In a meta-analysis and review of online learning spanning the years 1996 to 2008, authors from the US Department of Education found that students who took all or part of their classes online showed better learning outcomes than those students who took the same courses face-to-face. In these cases, it is important to note that there were many differences noted in the online and face-to-face versions, including the amount of time students spent engaged with course content. The authors concluded that the differences in learning outcomes may be attributed to learning design as opposed to the specific mode of delivery (Means, Toyoma, Murphy, Bakia, Jones, 2009).
Limitations and Opportunities
After examining the research comparing student learning outcomes in online education with the traditional classroom setting, there are many limitations that came to light, creating areas of opportunity for additional research. In many of the studies referenced, it is difficult to determine the pedagogical practices used in course design and delivery. Research shows the importance of student-student and student-teacher interaction in online learning, and the positive impact of these variables on student learning (Bernard, Borokhovski, Schmid, Tamim, & Abrami, 2014). Some researchers note that while many studies comparing online and traditional classroom learning exist, the methodologies and design issues make it challenging to explain the results conclusively (Mollenkopf, Vu, Crow, & Black, 2017). For example, some online courses may be structured in a variety of ways, i.e. self-paced, instructor-led and may be classified as synchronous or asynchronous (Moore, Dickson-Deane, Galyan, 2011)
Another gap in the literature is the failure to use a common language across studies to define the learning environment. This issue is explored extensively in a 2011 study by Moore, Dickson-Deane, and Galyan. Here, the authors examine the differences between e-learning, online learning, and distance learning in the literature, and how the terminology is often used interchangeably despite the variances in characteristics that define each. The authors also discuss the variability in the terms “course” versus “program”. This variability in the literature presents a challenge when attempting to compare one study of online learning to another (Moore, Dickson-Deane, & Galyan, 2011).
Finally, much of the literature in higher education focuses on undergraduate-level classes within the United States. Little research is available on outcomes in graduate-level classes as well as general information on student learning outcomes and perceptions of online learning outside of the U.S.
Conclusion
As we look to the future, there are additional questions to explore in the area of online learning. Overall, this research led to questions related to learning design when comparing the two modalities in higher education. Further research is needed to investigate the instructional strategies used to enhance student learning, especially in students with weaker academic preparation or from underrepresented backgrounds. Given the integral role that online learning is expected to play in the future of higher education in the United States, it may be even more critical to move beyond comparisons of online versus face to face. Instead, choosing to focus on sound pedagogical quality with consideration for the mode of delivery as a means for promoting positive learning outcomes.
References
Allen, I.E., Seaman, J., Poulin, R., & Straut, T. (2016). Online Report Card: Tracking Online Education in the United States [PDF file]. Babson Survey Research Group. http://onlinelearningsurvey.com/reports/onlinereportcard.pdf
Angelino, L. M., Williams, F. K., & Natvig, D. (2007). Strategies to engage online students and reduce attrition rates. The Journal of Educators Online, 4(2).
Ashby, J., Sadera, W.A., & McNary, S.W. (2011). Comparing student success between developmental math courses offered online, blended, and face-to-face. Journal of Interactive Online Learning, 10(3), 128-140.
Bernard, R.M., Borokhovski, E., Schmid, R.F., Tamim, R.M., & Abrami, P.C. (2014). A meta-analysis of blended learning and technology use in higher education: From the general to the applied. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 26(1), 87-122.
Cavanaugh, J.K. & Jacquemin, S.J. (2015). A large sample comparison of grade based student learning outcomes in online vs. face-fo-face courses. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Network, 19(2).
Clinefelter, D. L., & Aslanian, C. B. (2015). Online college students 2015: Comprehensive data on demands and preferences. https://www.learninghouse.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/OnlineCollegeStudents2015.pdf
Golubovskaya, E.A., Tikhonova, E.V., & Mekeko, N.M. (2019). Measuring learning outcome and students’ satisfaction in ELT (e-learning against conventional learning). Paper presented the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, 34-38. Doi: 10.1145/3337682.3337704
Kemp, N. & Grieve, R. (2014). Face-to-face or face-to-screen? Undergraduates’ opinions and test performance in classroom vs. online learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 5. Doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01278
Lyke, J., & Frank, M. (2012). Comparison of student learning outcomes in online and traditional classroom environments in a psychology course. (Cover story). Journal of Instructional Psychology, 39(3/4), 245-250.
Mayadas, F., Miller, G. & Senner, J. Definitions of E-Learning Courses and Programs Version 2.0. Online Learning Consortium. https://onlinelearningconsortium.org/updated-e-learning-definitions-2/
Means, B., Toyama, Y., Murphy, R., Bakia, M., & Jones, K. (2010). Evaluation of evidence-based practices in online learning: A meta-analysis and review of online learning studies. US Department of Education. https://www2.ed.gov/rschstat/eval/tech/evidence-based-practices/finalreport.pdf
Mollenkopf, D., Vu, P., Crow, S, & Black, C. (2017). Does online learning deliver? A comparison of student teacher outcomes from candidates in face to face and online program pathways. Online Journal of Distance Learning Administration. 20(1).
Moore, J.L., Dickson-Deane, C., & Galyan, K. (2011). E-Learning, online learning, and distance learning environments: Are they the same? The Internet and Higher Education. 14(2), 129-135.
Nichols, J., Shaffer, B., & Shockey, K. (2003). Changing the face of instruction: Is online or in-class more effective? College & Research Libraries, 64(5), 378–388. https://doi-org.proxy2.library.illinois.edu/10.5860/crl.64.5.378
Parsons-Pollard, N., Lacks, T.R., & Grant, P.H. (2008). A comparative assessment of student learning outcomes in large online and traditional campus based introduction to criminal justice courses. Criminal Justice Studies, 2, 225-239.
Pearson North America. (2018, June 25). How Online Learning Affects the Lives of Students. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mPDMagf_oAE
Protopsaltis, S., & Baum, S. (2019). Does online education live up to its promise? A look at the evidence and implications for federal policy [PDF file]. http://mason.gmu.edu/~sprotops/OnlineEd.pdf
Saad, L., Busteed, B., & Ogisi, M. (October 15, 2013). In U.S., Online Education Rated Best for Value and Options. https://news.gallup.com/poll/165425/online-education-rated-best-value-options.aspx
Stack, S. (2015). Learning Outcomes in an Online vs Traditional Course. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 9(1).
Seaman, J.E., Allen, I.E., & Seaman, J. (2018). Grade Increase: Tracking Distance Education in the United States [PDF file]. Babson Survey Research Group. http://onlinelearningsurvey.com/reports/gradeincrease.pdf
Slover, E. & Mandernach, J. (2018). Beyond Online versus Face-to-Face Comparisons: The Interaction of Student Age and Mode of Instruction on Academic Achievement. Journal of Educators Online, 15(1). https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1168945.pdf
Summers, J., Waigandt, A., & Whittaker, T. (2005). A Comparison of Student Achievement and Satisfaction in an Online Versus a Traditional Face-to-Face Statistics Class. Innovative Higher Education, 29(3), 233–250. https://doi-org.proxy2.library.illinois.edu/10.1007/s10755-005-1938-x
Tichavsky, L.P., Hunt, A., Driscoll, A., & Jicha, K. (2015). “It’s just nice having a real teacher”: Student perceptions of online versus face-to-face instruction. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 9(2).
Wiley Education Services. (n.d.). Top challenges facing U.S. higher education. https://edservices.wiley.com/top-higher-education-challenges/

Leave a Reply