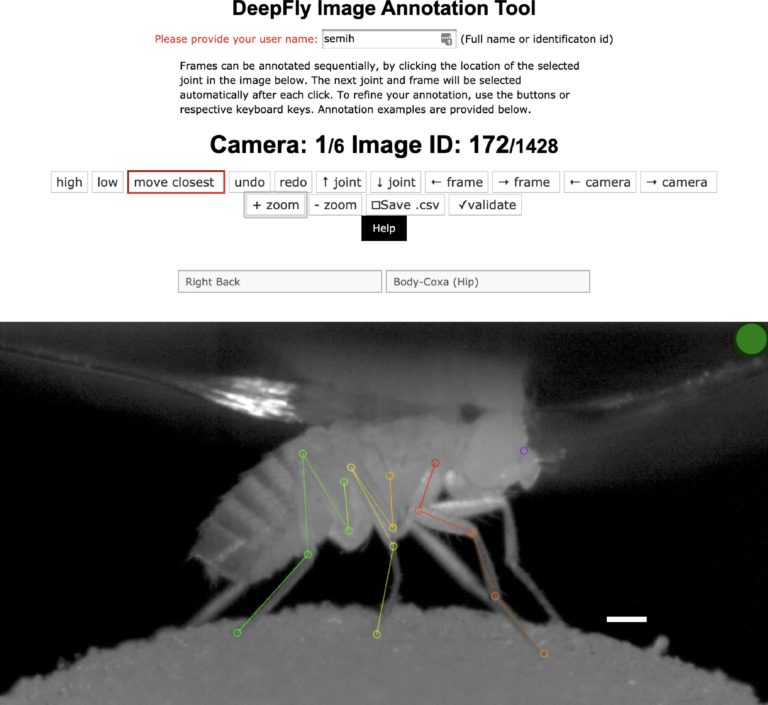
Semih Günel and colleagues have created a deep learning-based pose estimator for studying how neural circuits control limbed behaviors in tethered Drosophila. Appendage tracking is an important behavioral measure in motor circuit research. Up until now, algorithms for accurate 3D pose estimation in small animals such as Drosophila did not exist. Rather, researchers have had to use alternative approaches such as placing small reflective biomarkers on fly leg segments. While this method is appropriate for larger animals, implementing this strategy in drosophila-sized animals is motion limiting, labor intensive, and cannot estimate 3D information, therefore limiting the accuracy of behavioral measures. DeepFly3D is a PyTorch and PyQT5 based software designed to solve these issues and provide a user-friendly user interface for pose estimation and appendage tracking. DeepFly3D makes of use of supervised deep learning for 2D joint detection and a multicamera setup to iteratively infer 3D poses. This new approach allows for sub-millimeter scale accuracy of automated measurements. Amazingly, DeepFly3D is not limited to drosophila and can be modified to study other animals, such as rodents, primates, and humans. DeepFly3D therefore allows for versatile pose estimation while also permitting an extraordinary level of behavioral detail and accuracy. This research tool was created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the tool was described, and include an RRID in the Materials and Methods of your future publications. Project portal RRID:SCR_021400; Software RRID:SCR_021402 Learn more about DeepFly3d in eLife! Access the experimental data from this paper from the Harvard Dataverse! Check out the GiHub repository for the project.DeepFly3D
Read the Paper
Experimental Data
DeepFly3D GitHub
Have questions? Send us an email!