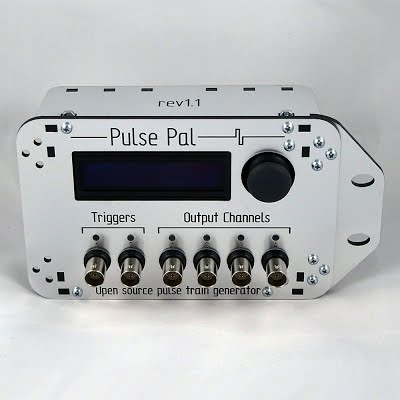
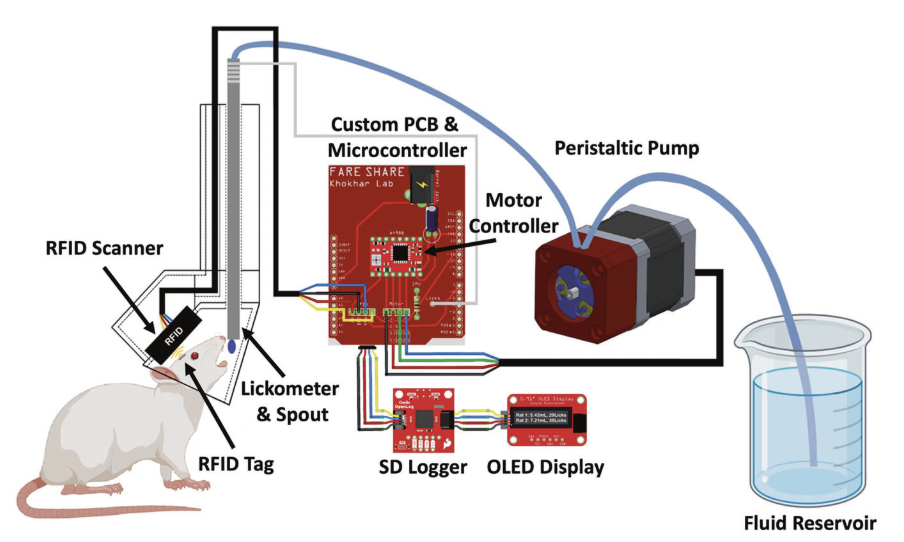
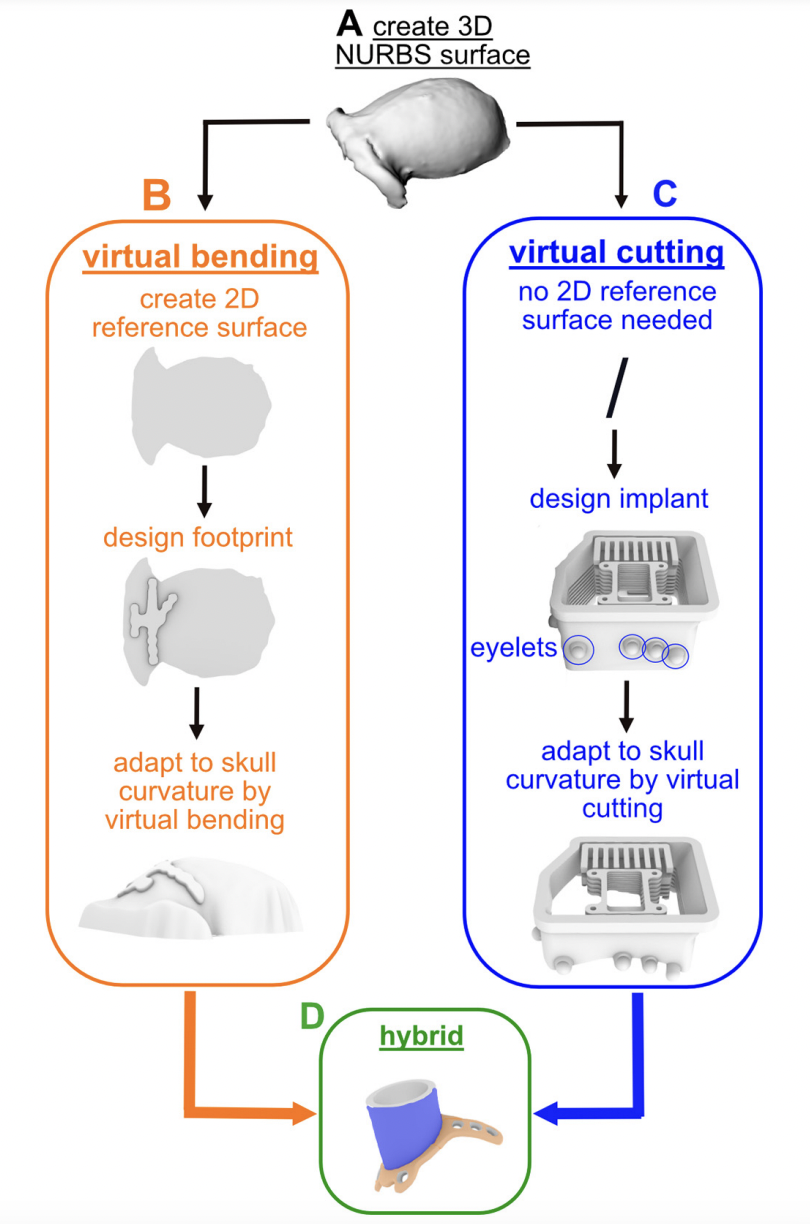
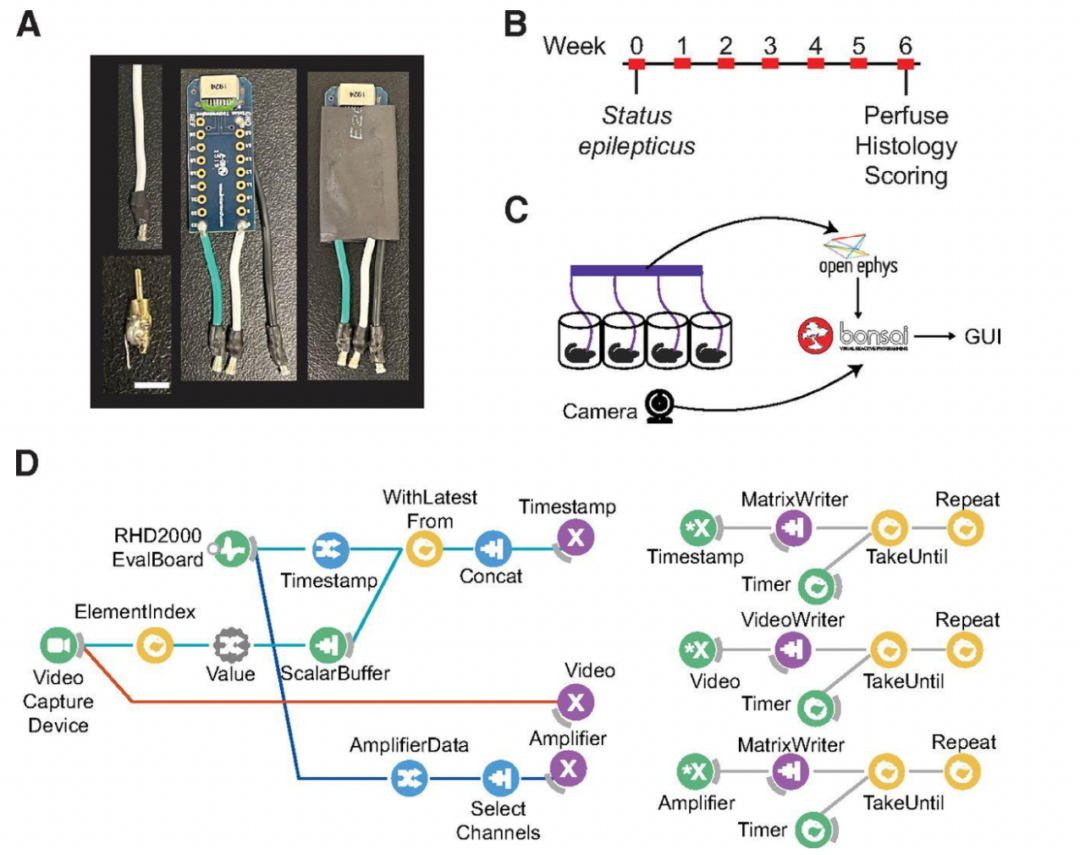
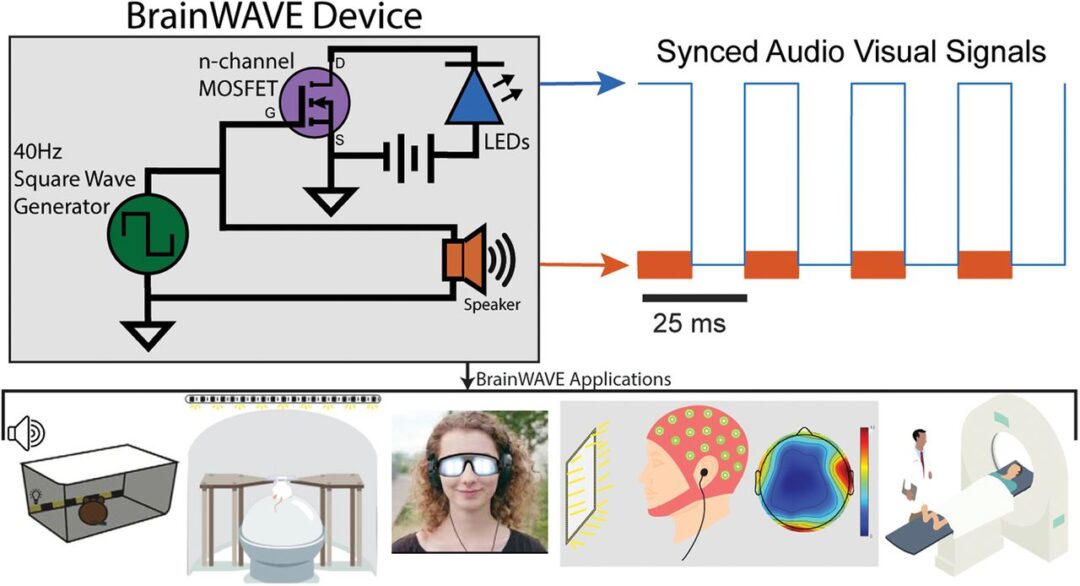
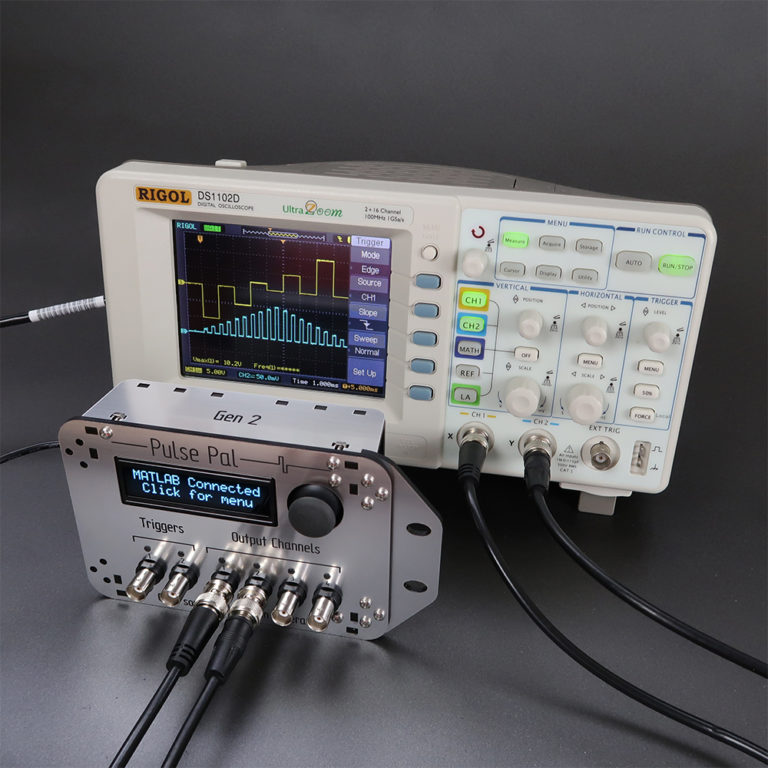
Josh Sanders has also shared the following with OpenBehavior regarding Pulse Pal, an open source pulse train generator. Pulse Pal and Bpod, featured earlier, were both created by Sanworks. Pulse Pal is an Arduino-powered device that generates precise sequences of voltage pulses for neural stimulation and stimulus control. It is controlled either through its APIs in MATLAB, Python and C++, or as a stand-alone instrument using its oLED screen and a clickable thumb joystick. Pulse Pal can play independent stimulus trains on its output channels. These trains are either defined parametrically, or pulse-wise by specifying each pulse’s onset time and voltage. Two optically isolated TTL trigger channels can each be mapped to any subset of the output channels, which can range between -10V and +10V, and deliver pulses as short as 100µs. This feature set allows Pulse Pal to serve as an open-source alternative to commercial stimulation timing devices, i.e. Master 8 (AMPI), PSG-2 (ISSI), Pulsemaster A300 (WPI), BPG-1 (Bak Electronics), StimPulse PGM (FHC Inc.) and Multistim 3800 (A-M Systems). Because Pulse Pal is an Arduino-powered device, modifying its firmware for custom applications is within the capabilities of most modern Neuroscience research labs. As an example, the Pulse Pal’s Github repository provides an alternative firmware for the device, that entirely repurposes it as a waveform generator. In this configuration, a user can specify a waveform, frequency, amplitude and max playback duration, and toggle playback by TTL pulse with ~100µs latency. The firmware can also loop custom waveforms up to 40,000 samples long. Pulse Pal was first published in 2014, by Josh Sanders while he was a student in Kepecs Lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. A significantly improved second-generation stimulator (Pulse Pal 2) became available in early 2016, coincident with the opening of Sanworks LLC. Over the past year, >125 Pulse Pal 2 devices were sold at $545 each by the Sanworks assembly service, while several labs elected to build their own. The initial success of this product demonstrates that fully open-source hardware can make headway against closed-source competitors in the Neuroscience instrumentation niche market. This research tool was created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the tool was described, and include an RRID in the Materials and Methods of your future publications. Project portal RRID:SCR_021576; Software RRID:SCR_021611 Check out projects similar to this!Pulse Pal
Read the paper!
Have questions? Send us an email!
Read more in their paper published in Frontiers in Neuroengineering!