Basic Nutrition
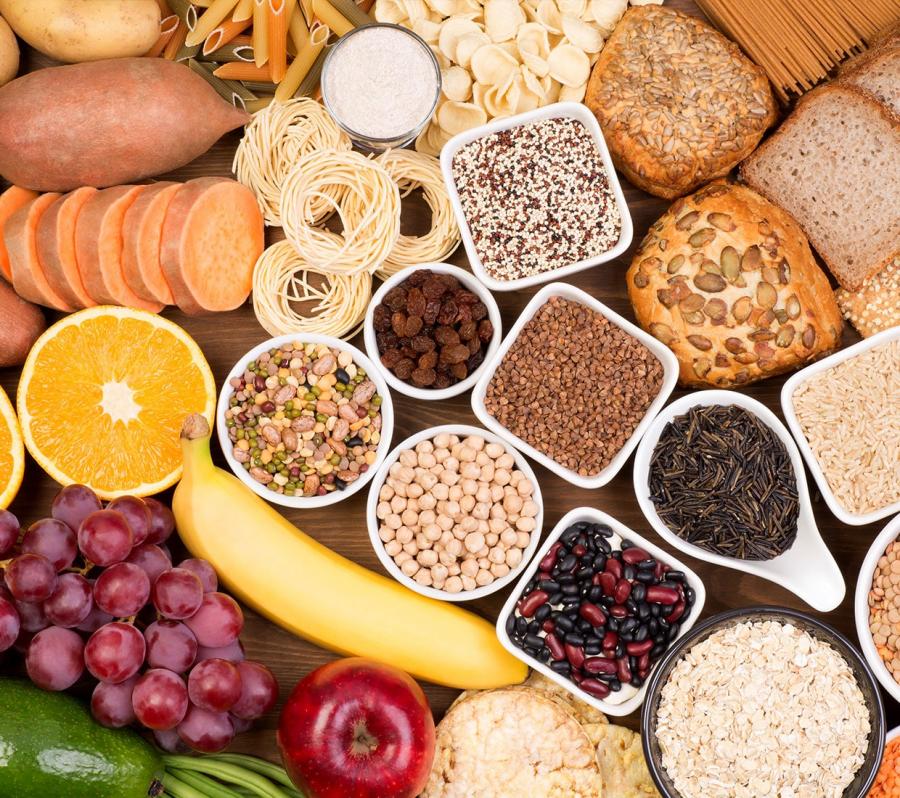

Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source.
- Extra carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen. When your body is in need of energy, it will first use stored glycogen by turning it back into glucose.
- When glycogen storage has reached its max, extra energy is stored as fat. Besides providing the body with energy, carbs also play a role in cell and tissue function.
- Foods that contain carbs include grains (bread, pasta), fruit, vegetables, dairy, and sweeteners (honey, table sugar).
- Starches are a type of carbohydrate and you can find them in potatoes, legumes, and grains (rice, corn, wheat).
- Fiber is also a type of carbohydrate that helps with digestive function and can help lower cholesterol. Foods like legumes, whole grains, and many fruits and vegetables are rich in fiber.
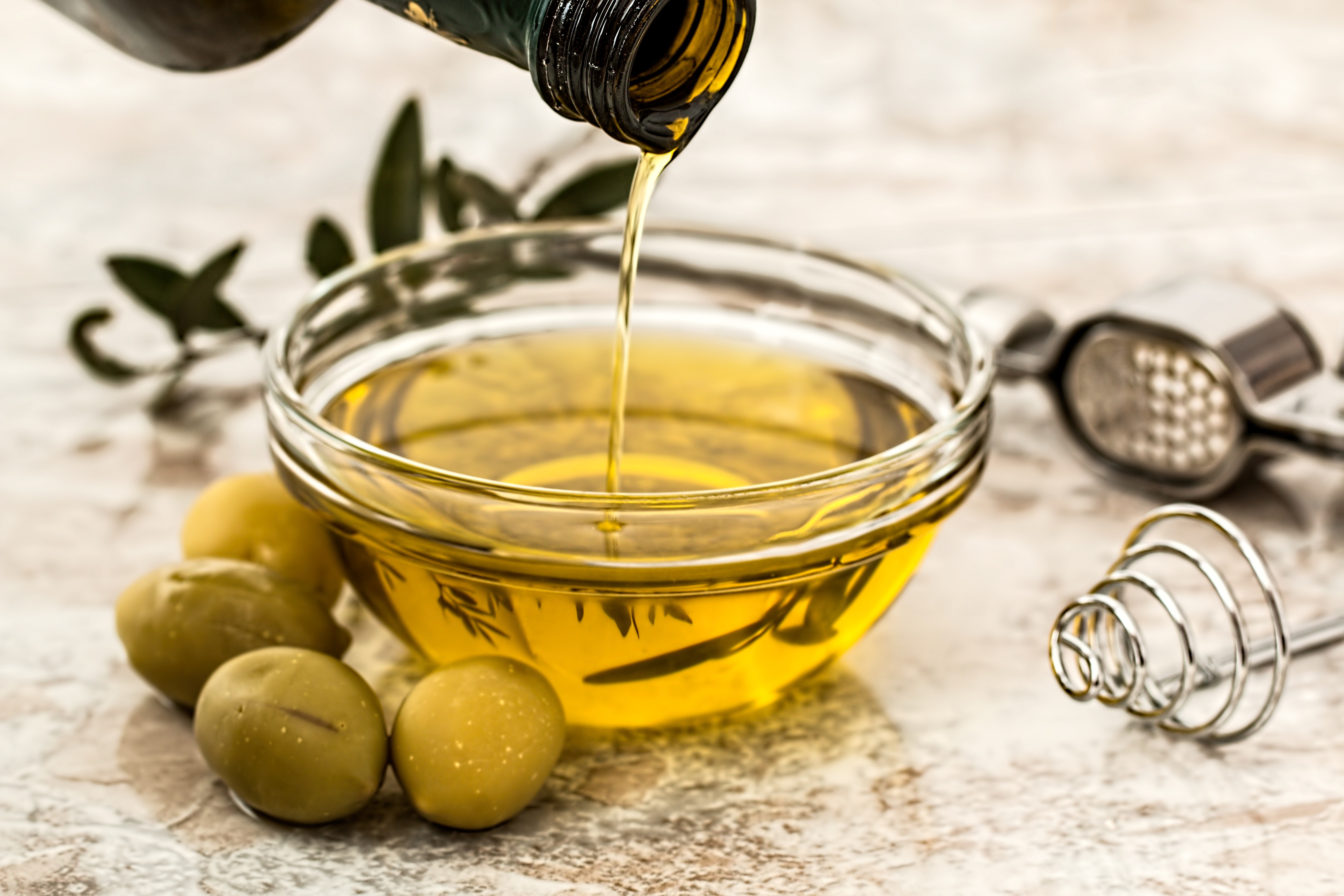

Fats
- Dietary fat is a type of lipid called a triglyceride.
- Fat also provides the body with energy and is important for energy storage and insulating the body. Fat also plays an important role in cell function and the intake of fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamins A and D.
- There is an assumption that fat is bad for the body-this is incorrect. Fat is vital for bodily function but there are certain types of fat that you should show preference to.
- You can find fat in meat, eggs, oil, nuts and seeds, some vegetables and fruits (coconuts, avocados), and dairy products.
- Unsaturated fats are good for the body and help prevent heart disease. You can find unsaturated fats in many types of oils (olive, canola, sunflower), seeds and nuts, fatty fish (salmon), and avocados. Unsaturated fats are usually liquid at room temperature. Saturated fats and trans fats can cause harm to the body and play a role in many chronic diseases.
- Saturated fats can be found in meats like beef, palm and coconut oil, butter, and other dairy products. Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature.
- Trans fats are artificially made by adding hydrogen to unsaturated fats and making them solid. Trans fats can be found in many processed food items but there is a movement to use less of them.

Protein
- Protein plays a vital role in repairing and building the body’s tissues.
- Proteins are made up of amino acids and there are nine essential amino acids.
- Extra protein can’t be stored by the body like fat and carbohydrates. This means it is important to meet your daily value in the nutrient as there is no extra supply when you start becoming deficient.
- Foods like meat, eggs, legumes, nuts and seeds, and soy products are good sources of protein.
- Proteins from animal sources usually contain all essential amino acids, while many vegetable proteins do not (except soy products). Individuals following a plant-based diet should be mindful of getting a variety of different types of vegetable proteins to make sure they are getting all their essential amino acids.
Cook with oils instead of
butter to avoid saturated
fats.
When choosing what type of
bread or pasta to eat, look for
whole-grain options as they
will also provide you with
fiber.
Eat lean meats and/or plant
proteins to reduce your
intake of saturated fats.
Eat carbs from grains, green
vegetables, starches, and
legumes (less sweet carbs) for
a more extended release of
energy.
NUTRITION LABELS
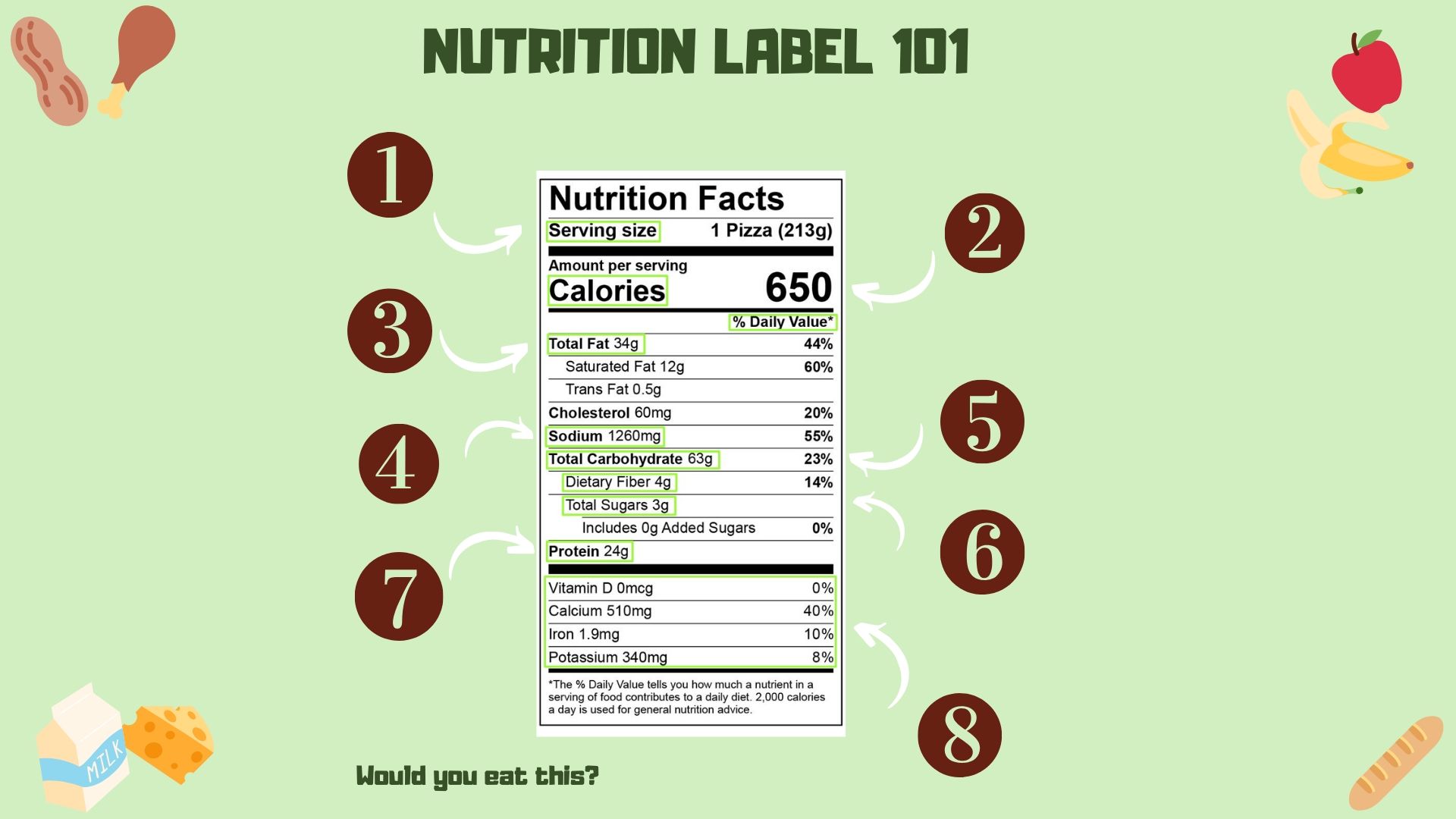
1. Everything below is in reference to this measurement. Make changes when eating more or less.
2. Calories are a measure of energy. You burn the calories that you eat through physical activity. Consider this when looking at food options.
3. Fat is not always bad. Try to look for foods with unsaturated fat. Reduce your intake of saturated fat. Avoid trans fat.
4. Salt plays a big role in blood pressure and other chronic diseases. Try to keep your sodium intake under 2300 mg a day.
5. Carbs are the main energy source for the body. Things like grains, sugar, starchy foods, and dairy are where you usually find them.
6. Sugar is a type of carb. Too much can increase blood sugar levels. Try to stick to fruits which have fiber and vitamins along with sugar.
7.Protein plays a role in cellular and muscle function. Eat beans, nuts, eggs, and meat if you want more protein in your diet.
8. All food has a different composition of the vitamins and minerals it contains. They are all important to the body for different reasons. Being deficient in a vitamin can lead to noticeable health effects. This is one of the many reasons why eating a balanced diet is so important.
ADDITIVES
Additives are often found in processed food. They can be used for a number of things, from preservation to coloring. Some additives can lead to unwanted health effects. Here are a few:
Sodium nitrate: It is used to preserve meats by preventing the growth of bacteria. However, it has been linked to an increase in gastrointestinal issues. Also, it can lead to the hardening of arteries, which can cause heart disease.
Trans fats: Trans fats can increase the stability of food. They are linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Yellow no. 5 and 6: Used to add color to foods such as candy. The colorings can lead to allergic reactions in those with asthma. Additionally, according to the Center for Science in the Public Interest, studies have shown that the colorings have caused tumors in mice and contain cancer-causing agents.


